June 13, 2017

The Iceberg Cometh: Welcome to Sickville, USA
In the western suburbs outside Minneapolis, two men lead average lives. Surveying them as part of the general population, no health system, insurer or policy maker would notice anything that might be alarming. Yet, when it comes to the healthcare costs they will incur over the next few years, they are ticking time bombs waiting to go off.
Their names are Matt and Jim. In terms of traditional health data, they’re so indistinguishable, they may as well be the same person. They’re non-smokers and slightly overweight, like many middle-aged American men, but they appear to be in good health with long lives ahead of them. They live in the same county and are employed by mid-sized companies with comprehensive health plans and manageable deductibles.
Then one day, Matt and Jim visit their respective primary care physicians for wellness checkups. The news is not good. Blood tests reveal higher than normal glucose levels. Matt and Jim are pre-diabetic and well on their way to developing hypertension unless they change their lifestyle and eating behaviors significantly.
The news is a shock. Until now, 58 didn’t seem very different from 50. But genetic predispositions and the accumulation of years of bad habits are taking their toll. It’s not too late, however. The doctors give each man a health improvement plan. If they follow it, they will avoid serious (and costly) health conditions down the road.
Which of these two men will heed their doctor’s advice and make the dramatic changes necessary to get their blood sugar levels and body weight under control? With big data, we now know the answer.
It’s Matt. Because he has a dog.
The Problem with Icebergs
Matt and Jim are not alone, and they are not the tip of the iceberg. Instead, they represent the invisible problem below the water line, a threat so enormous it could sink any Titanic including the American healthcare system.
That iceberg is dead ahead.
We know what’s above the waterline. 20% of the American population absorbs around 80% of the national healthcare spend.[1] That group is largely made up of people who are chronically ill, with diseases like diabetes and hypertension, or who have some form of cancer.
Increasingly, the healthcare system devotes resources, attention and innovation to managing the care of patients with cancer or chronic illness. There is good evidence that a variety of different approaches, ranging from Medicare Advantage programs to new venture-backed primary care services, provide those patients with better healthcare at less cost.
The healthcare system is not skillful, however, at predicting which people will end up needing such services. It also vastly underestimates the size of that population. The implicit assumption behind the “20%” problem is that the remaining 80% of the population is fine and most of those people do not require meaningful interventions.
It turns out, this assumption is not even close to being true. The iceberg is much larger and more threatening than it would appear above the waterline.
The Ranks of the Walking Sick
Two recent studies by Harvard University and the Mayo Clinic indirectly pointed to the scale and nature of the problem the healthcare system faces in dealing with ticking time bombs.
The Harvard study[2] focused on the behavioral determinants of cancer while the Mayo study[3] looked at the behavioral determinants of chronic illness. Each study identified the same five behaviors.
A person is likely to avoid cancer or chronic illness if they:
- Are a non-smoker
- Get around 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week
- Have a relatively normal body fat percentage
- Enjoy a reasonably healthy diet
- Drink alcohol moderately or not at all
As a list of ideal lifestyle activities, this seems reasonable and not very daunting. Both studies also offer good odds for people who adopt such a lifestyle. A person who consistently demonstrates four or five of the behaviors cuts their risk of cancer by 60% and the risk of most chronic illnesses by 80%.
Carrot Health’s examination of publicly available health data reveals the bad news. The percentage of the overall population that exhibits all five of those behaviors is a miniscule 2.7%. In contrast, the percentage of the population that demonstrates none of those behaviors is 11%. The remaining 87% of Americans are at serious risk of developing chronic illness or cancer.

Healthcare Data vs Consumer Data
Current healthcare data is insufficient for understanding, predicting and meeting the healthcare needs of most Americans.
Traditional healthcare data measures health status but misses 90% of the factors that determine health. Missing from current health charts are “social and physical determinants of health” related to environmental, behavioral, economic and demographic characteristics. These factors shape and influence an individual’s current and future health status.
Examples of Social Determinants include:
- Availability of resources required to meet daily needs, like education, job opportunities, living wages, and access to healthy foods
- Social norms and attitudes, including discrimination and microaggressions
- Public safety and exposure to crime, violence, or social disorder
- Social support and interactions/connections within community/social isolation
- Media and access to emerging technologies
- Residential segregation or concentrated poverty
- Quality schools, language/literacy, graduation rates
- Economic stability/instability
- Access to quality child care
- Incarceration
- Access to health care providers
Examples of Physical Determinants include:
- Natural environment such as green space, weather, climate change
- Built environment such as building, sidewalks, transportation
- Access to transit options
- Worksites, schools, parks and recreational settings
- Housing and neighborhoods/community design
- Exposure to toxic substances and other physical hazards
- Urban design and zoning ordinances
- Physical barriers, especially for elders and people with disabilities
- Aesthetic elements such as lighting, trees, benches, places to gather
For years, retail companies have curated data in order to target consumers, identify new markets and predict consumer trends. The famous “Target” story illustrates the power of that approach.
A father called Target to complain that it was sending his daughter coupons for pregnancy-related products. Target’s consumption algorithm picked up on a change in her purchase patterns and identified key items, such as unscented lotion, to determine that pregnancy was likely. Leveraging that information, Target’s sales force initiated appropriate action to meet that customer’s needs. The father later apologized to Target after discovering that his daughter was, in fact, pregnant.[4]
In contrast, healthcare data reveals little beyond the surface. It focuses on treating immediate needs and reacting to symptoms. To the healthcare system Matt and Jim may as well be the same person. To Target or other big retailers, Matt might be a bargain hunter who is thinking about remodeling his bathroom, while Jim only shops for jeans, underwear and socks when he must.
It would be a waste of resources for a retail company to treat these men the same. It is just as unproductive for a health company to treat them alike.
Peeling the Onion
To understand Matt’s and Jim’s health needs and predict their health risks, we must peel back the onion and see how they live. This requires augmenting healthcare data with survey, demographic and retail data. The chart below illustrates the wide range of available data sources.
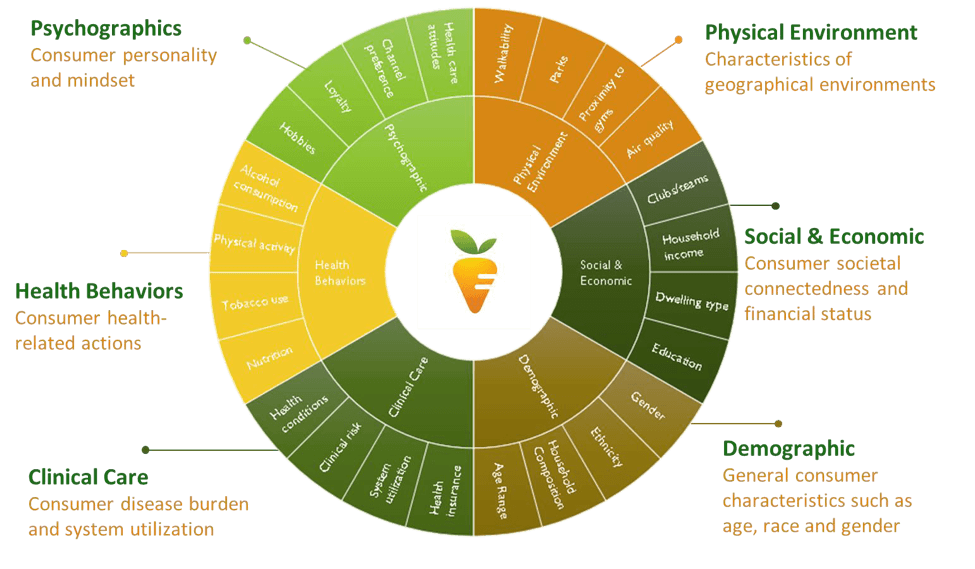
Unlike healthcare data, consumer data offers a window into the social and physical determinants that shape individual circumstance. Leveraging such data, Carrot Health has developed a national database for every adult citizen in the US, approximately 250 million people.
Data analytics reveal behavioral activities and social/physical circumstances that correspond to health. For example, physical inactivity has enormous correlation with diabetes. Carrot Health’s data set identifies individuals prone to physical inactivity across the country and correlates their inactivity with incidence of diabetes (see charts below).
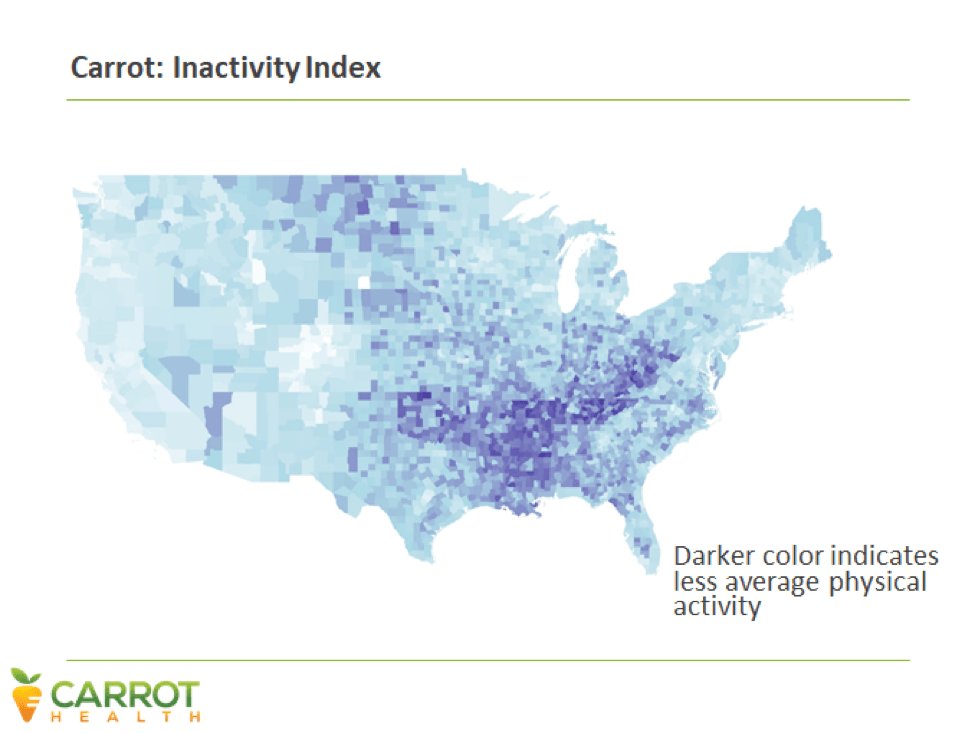
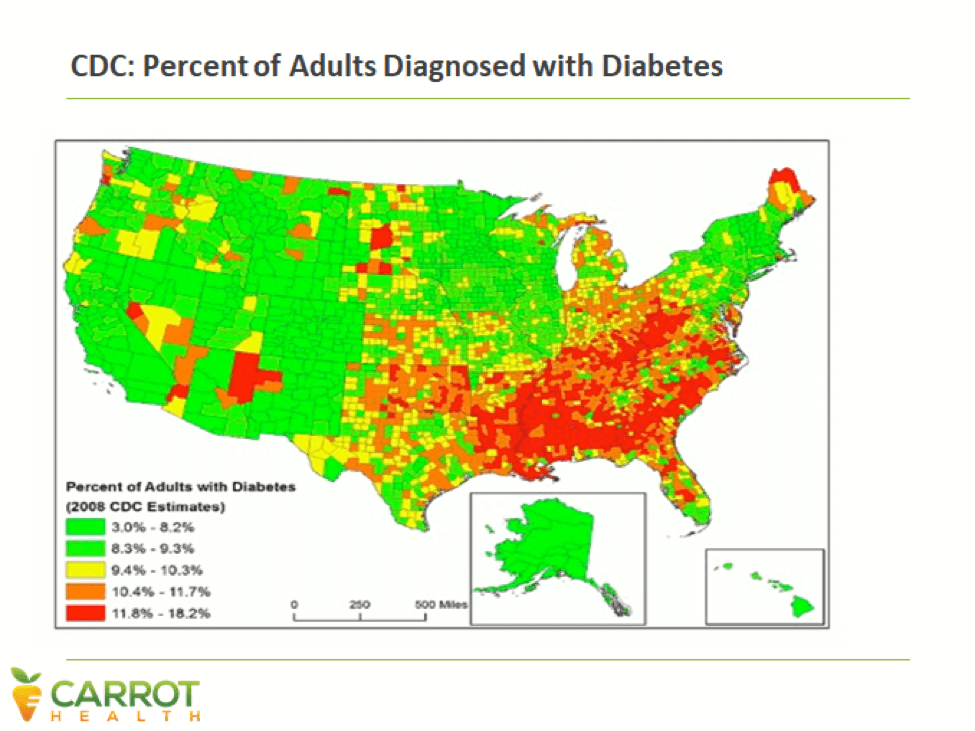
These sweeping, regional looks are valuable, but data analytics goes much deeper, down to individual household behaviors.
We can use consumer data to predict the likelihood that a specific individual will develop a chronic illness or cancer. We can also predict the likelihood that someone will avert that illness by adopting new behaviors or utilizing resources available to them.
This is how we know that Matt, not Jim, is more likely to successfully defuse his ticking time bomb and avoid diabetes and hypertension.
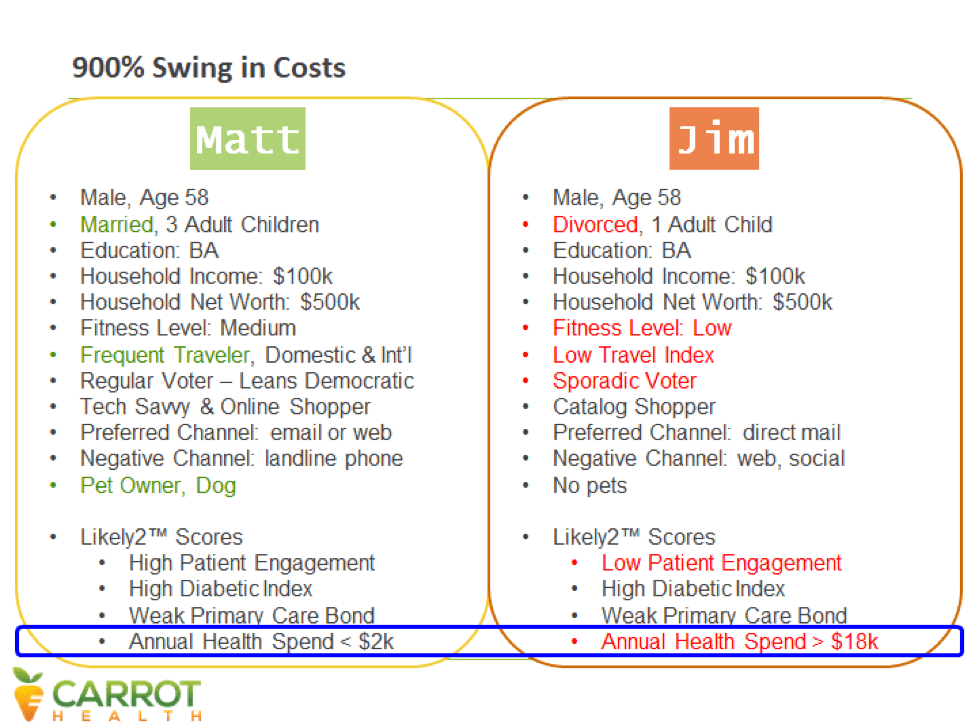
While the two men are nearly identical according to their healthcare data, their consumer data reveals a different picture.
In most ways, Matt and Jim are quite similar. They live in the same neighborhood with the same access to parks and grocery stores and the same length of commute. Both have well-paying white collar jobs with solid companies. Both are ambitious workaholics who make frequent business trips.
In important ways, however, they differ from one another. While Matt is married, Jim is recently divorced. Matt has three children, while Jim has one. Matt was raised in Minnesota but Jim is from Massachusetts originally and has little extended family in the area. Matt is active in local politics and campaigns for candidates he supports. Jim only votes in Presidential elections. Matt has an energetic four-year old Lab named Einstein while Jim doesn’t have any pets.
Matt and Jim’s social differences influence their health status. Jim is more socially isolated than Matt and probably lacks the emotional support and encouragement needed to adopt and adhere stick to a health improvement plan. Jim is also more likely, to present co-morbid behavioral health issues that correspond with depression, substance abuse and physical inactivity.
By contrast, Matt’s community involvement and support are positive motivators for adopting and sustaining needed behavioral changes. Moreover, Matt’s dog Einstein, needs vigorous daily walks so Matt moves around more.
Knowing their differing risk factors and motivations, a health company can develop more appropriate interventions for each man, and likely improve their health status.
The Missing Big Picture
The average American is inactive more than eight waking hours per day. No age group older than 30, on average, undertakes more than 30 minutes of moderate or vigorous activity per day.”[5] According to a 2012 circular from the American Heart Association, 65 % of American adults routinely “sit instead of stand, drive instead of walk, and ride the elevator instead of walking up stairs.”[6]
Socio-economic realities foster unhealthy lifestyles and rising obesity. Lower income neighborhoods traditionally offer fewer healthy food choices. Financial circumstances often limit nutritional choices. These factors have lasting dietary impacts. Research indicates that the earlier children are exposed to junk food, the more likely they are to suffer dangerous, life-long health problems.[7] Societal disconnection also incubates disease. Socially isolated individuals are prone to depression and less likely to exercise and eat well.
From a pure economic standpoint, U.S. healthcare treats the bi-products of disease, not its root causes (see chart below).
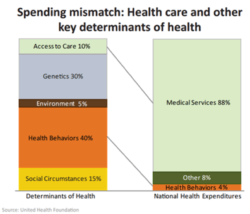
United Health Foundation. (2012). America’s health rankings. Retrieved from: http://www.americashealthrankings.org/MN/2012
We do very little to prevent people from entering the ranks of the chronically ill even though they represent billions in future healthcare spending.
Multifaceted Solutions for a Multifaceted Problem
By examining the social, demographic, and other determinants of health with data analytics, healthcare professionals can determine which populations are most at risk, and design cost-effective interventions for improving their health. The challenge for health companies is to identify meaningful risk drivers for individuals and develop effective approaches for engaging those consumers.
Here’s the scary conclusion. As daunting as it is, America could “fix” healthcare delivery (right care, right time, right place, right price) and still experience lower health status and rising health expenditures. Failure to improve social determinants of health positions the country for ever-higher levels of chronic disease, lower productivity and greater inequality.
This is not an acceptable future state. Big data analytics provide a formidable weapon for identifying and combatting root causes of disease. It’s time to unleash big data’s power to influence behavioral change, so America’s future can be healthier and happier.
Sources
[1] http://www.countyhealthrankings.org/our-approach
[2] http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/article-abstract/2522371
[3] http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-blog/lifestyle-changes-for-heart-%20health/bgp-20198584
[4] https://www.forbes.com/sites/kashmirhill/2012/02/16/how-target-figured-out-a-teen-girl-was-pregnant-before-her-father-did/#78e5531f6668
[5] http://www.theverge.com/2015/1/22/7870707/bmj-sedentary-job-health-riskst
[6] http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/126/1/e3.full
[7] http://www.medicaldaily.com/unhealthy-eating-habits-begin-early-infancy-formula-feeding-junk-food-should-be-avoided-308916